Dengue
Introduction
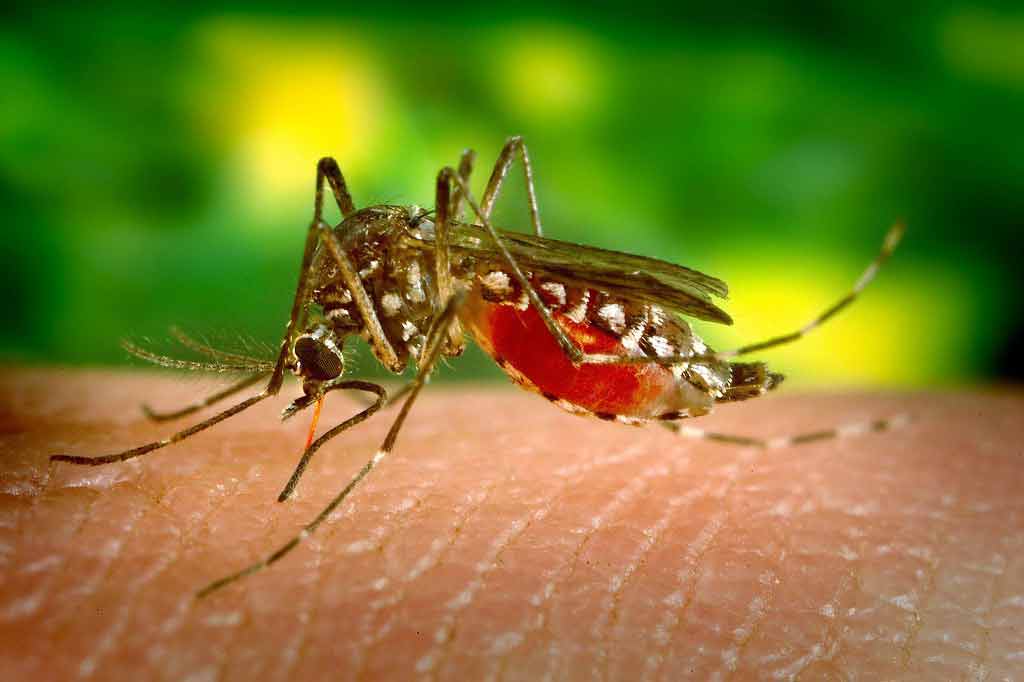
Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes. It's widespread in many parts of the world.
In most people the infection is mild and passes in about a week without causing any lasting problems. But in rare cases it can be very serious and potentially life threatening.
There's no specific treatment or widely available vaccine for dengue, so it's important to try to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes when visiting an area wherethe infectionis found.
Where dengue is found
Dengue is found in parts of:
- southeast Asia
- the Caribbean
- the Indian subcontinent
- South and Central America
- Africa
- the Pacific Islands
- Australia
Use travel destination guide to find out if dengue is a risk in a country you're planning to visit.
How dengue is spread
Dengue is spread by infected mosquitoes, usually the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus varieties.
These mosquitoes bite during the day, most often early in the morning or in the earlyevening before dusk.
They're often found living around sources of stagnant water in built-up areas, such as wells, water storage tanks or old car tyres.
Dengue isn't spread from person to person.
You can get it again if you've had it before, as you'll only be immune to one particular variant of the virus.
Introduction
Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes. It's widespread in many parts of the world. In most people the infection is mild and passes in about a week without causing any lasting problems. But in rare cases it can be very serious and potentially life threatening.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dengue usually develop suddenly 4 to 10 days after becoming infected like; a high temperature (fever), severe headaches, pain behind the eyes, etc. The symptoms normally pass in about a week, although you may feel tired and slightly unwell for several weeks afterwards.
Severe Dengue
In rare cases dengue can be very serious and potentially life threatening. This is known as severe dengue or dengue haemorrhagic fever. People who've had dengue before are thought to be most at risk of severe dengue if they become infected again.
Prevention
There's currently no widely available vaccine for dengue. You can prevent it by avoiding being bitten by mosquitoes, use insect repellent, wear loose but protective clothing, etc.
Treatment
There's no cure or specific treatment for dengue. Treatment involves relieving your symptoms while the infection runs its course. You can usually look after yourself at home. Take paracetamol to relieve pain and fever, drink plenty of fluids, etc.
Patient story: "I wouldn't want to repeat the experience of having dengue."
The story of Hugh Wilson, who came down with dengue while on holiday in Thailand. Hugh and his partner were staying in Krabi insouthern Thailand when Hugh started to experience symptoms.







 Subscribe
Subscribe Ask the doctor
Ask the doctor Rate this article
Rate this article Find products
Find products